14+ many plants have waxy coatings on some surfaces
In some plants the waxy. This coating reduces water loss because it is not water-permeable.

Plants That Live In The Desert Twinkl Teaching Wiki
Many plants have waxy coatings on some surfaces.
. This coating reduces water loss because it is not water permeable. This waxy coating is which of the following types. They store metabolic energy protect against dehydration and pathogens carry electrons absorb light.
Lipids are ubiquitous in plants. This coating reduces water loss because it is not water-permeable. This coating reduces water loss because it is not water-permeable.
This waxy coating is which of the following types of organic molecules. This waxy coating is which of the following types of organic molecules. Answered Many plants have waxy.
Many plants have waxy coatings on some surfaces This coating reduces water loss from BIOLOGY 1 at Mcarthur High School. Succulent plants store water in fleshy leaves stems or roots. Many plants have waxy coatings on some surfaces.
Published in category Biology 13072021. This waxy coating is which of the following types of organic molecule. Many plants have waxy coatings on.
1 on a question Many plants have waxy coatings on some surfaces. Many plants have waxy coatings on some surfaces. This coating reduces water loss because it is not water-permeable.
Ratings 100 3 3 out of 3 people found this document helpful. The purpose of this covering is to help the plant retain water. This preview shows page 5 - 7 out of 17 pagespreview shows page 5 - 7 out of 17 pages.
What do you call a plant that has needles. In arid regions that is very. This preview shows page 5 - 7 out of 17.
Many plants have waxy coatings on some surfaces. 1 on a question Many plants have waxy coatings on some surfaces. This coating reduces water loss because it is not water-permeable.
Many plants have waxy coatings on some surfaces. This waxy coating is which of. The waxy covering on plant leaves young stems and fruit is called the cuticle.
Many plants have waxy coatings on some surfaces.
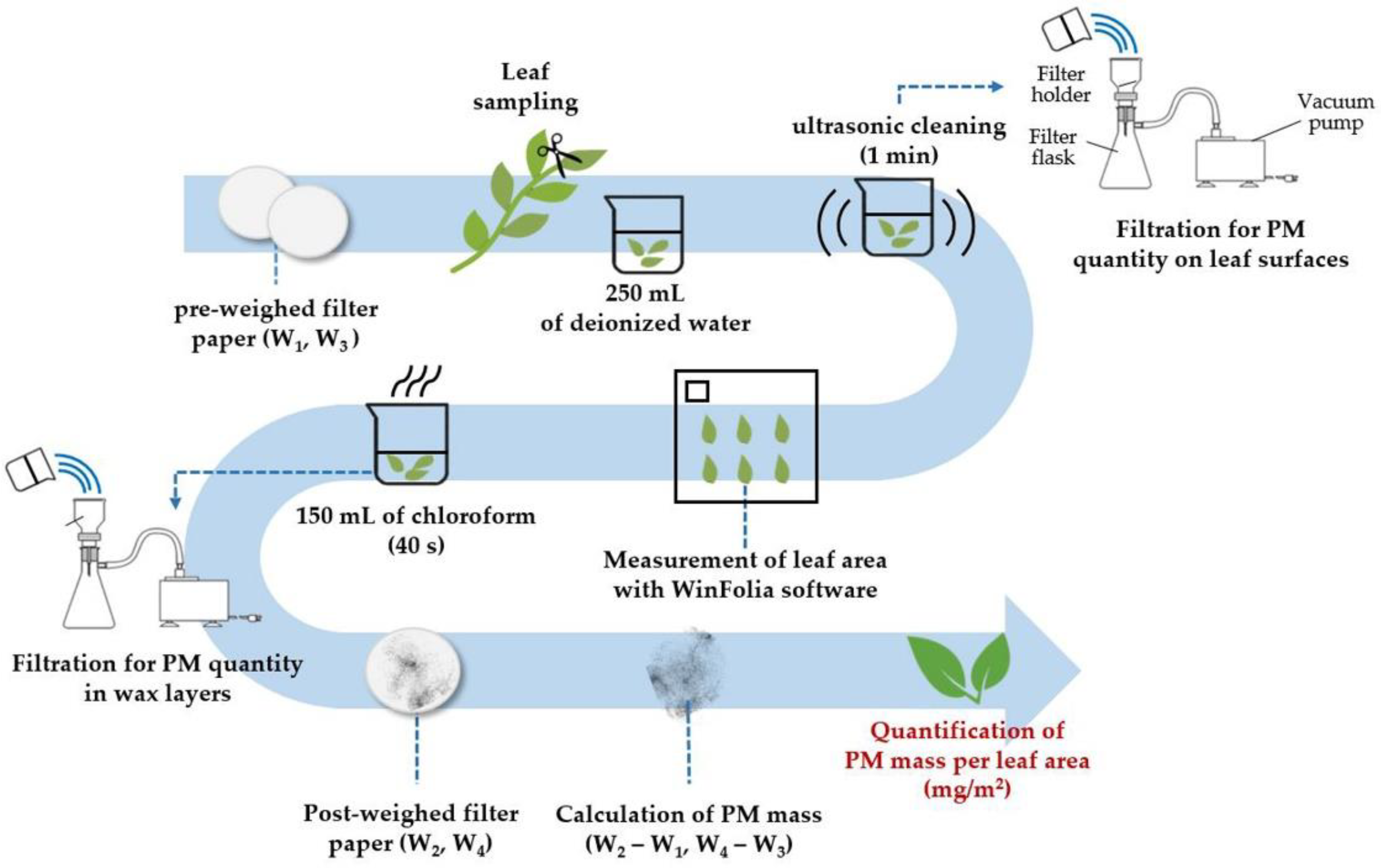
Forests Free Full Text Surface Based Analysis Of Leaf Microstructures For Adsorbing And Retaining Capability Of Airborne Particulate Matter In Ten Woody Species Html

Plant Surfaces Structures And Functions For Biomimetic Innovations Abstract Europe Pmc
Solved Many Plants Have Waxy Coatings On Some Surfaces This Coating Reduces Water Loss Because It Is Not Water Permeable This Waxy Coating Is Considered Which Biomolecule A Lipid C Nucleic Acid

Solved Many Plants Have Waxy Coatings On Some Surfaces This Coating Reduces Water Loss Because It Is Not Water Permeable This Waxy Coating Is Considered Which Biomolecule A Lipid C Nucleic Acid

Many Plants Have Waxy Coatings On Some Surfaces This Coating Reduces Water Loss Because It Is Not Brainly Com
Are There Any Risks Associated With Keeping Plants Indoors Quora

Unit 4 Practice Part 5 Biology Quiz Quizizz

Many Plants Have Waxy Coatings On Some Surfaces This Coating Reduces Water Loss Because It Is Brainly Com

Plant Surfaces Structures And Functions For Biomimetic Innovations Springerlink

Superhydrophobic And Superhydrophilic Plant Surfaces An Inspiration For Biomimetic Materials Philosophical Transactions Of The Royal Society A Mathematical Physical And Engineering Sciences

Solved Many Plants Have Waxy Coatings On Some Surfaces This Coating Reduces Water Loss Because It Is Not Water Permeable This Waxy Coating Is Considered Which Biomolecule A Lipid C Nucleic Acid
Are There Any Risks Associated With Keeping Plants Indoors Quora
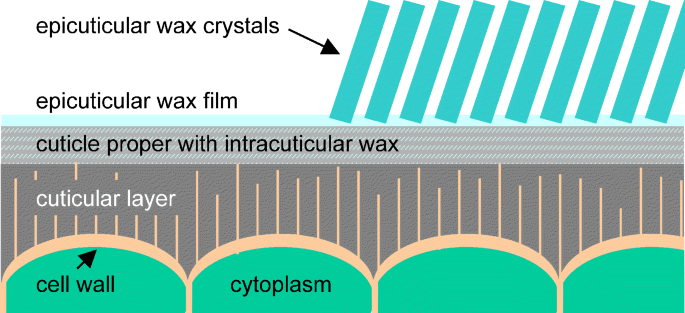
Plant Surface Properties In Chemical Ecology Springerlink
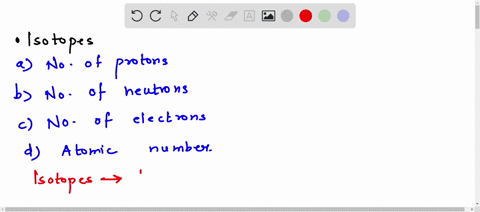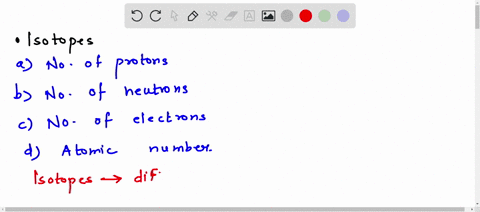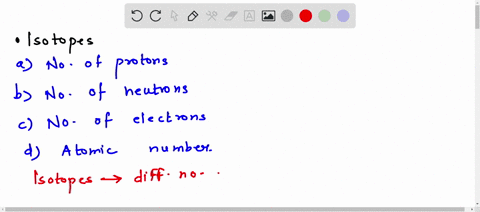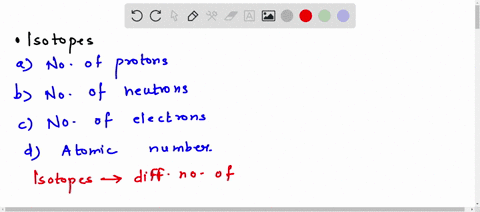
Solved Many Plants Have Waxy Coatings On Some Surfaces This Coating Reduces Water Loss Because It Is Not Water Permeable This Waxy Coating Is Which Of The Following Types Of Organic Molecules

The Hydrophobic Coatings Of Plant Surfaces Epicuticular Wax Crystals And Their Morphologies Crystallinity And Molecular Self Assembly Sciencedirect

Plant Surfaces Structures And Functions For Biomimetic Innovations Abstract Europe Pmc
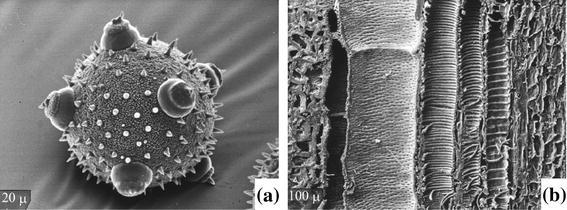
Plant Surfaces Structures And Functions For Biomimetic Innovations Springerlink